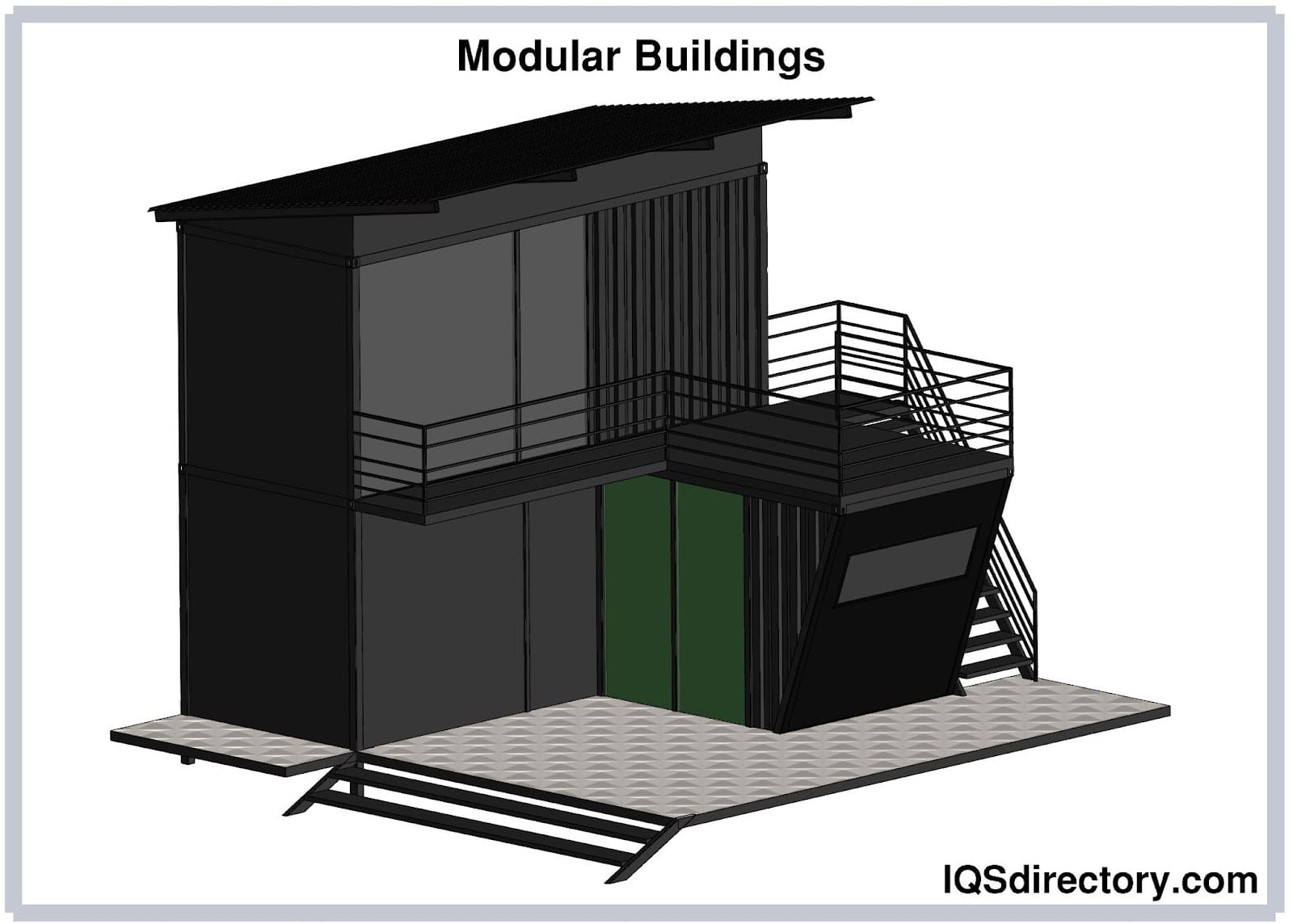
Modular buildings are a broad class of prefabricated buildings. Modular buildings are made up of movable sections known as modules and other factory-made components. Unlike traditionally constructed buildings, modular buildings, also known as prefab buildings, prefabricated buildings, or pre-engineered buildings, can move from concept to constructed structures in a matter of weeks. Read More…
As a modular building manufacturer, including inplant modular offices, exterior steel buildings, guard buildings, fork liftable and crane liftable buildings, multi-level buildings and mezzanines, Abtech offers turnkey installations or packages for install by end user. Our modular structures are constructed of steel, are free-standing & manufactured under strict quality control methods.

We offer a wide variety of affordable modular buildings for your convenience. Our engineers are determined to bring you a product with a great value and exceptional customer service. We have been around since 1954 providing portable buildings that are made out of steel.

Our booths and partitions are available in solid surface, stainless steel, solid plastic, solid phenolic, high pressure laminate, and metal powder coated. Our washroom accessories also include combo towel waste units, paper towel dispensers, waste receptacles, soap dispensers, mirrors, warm air hand dryers, toilet tissue dispensers, toilet seat cover dispensers, grab bars, bathroom accessories,...

Morgan Buildings can meet just about any modular building need. For over 60 years and 3 generations Morgan has been a pioneer and leader in modular design and construction. As a fully integrated family-operated company we design, build, transport and install modular buildings around the country and the world. From guard houses to 2-story housing complexes and everything in between we have the...

Donobrog has been a leading supplier of high-quality prefabricated modular buildings and modular offices since 1985. We offer single offices, 2-story multiunit enclosures and noise enclosures in a variety of sizes, styles and configurations. Call today for more information!

At Pope Industries Inc., we present ourselves as dedicated manufacturers of modular buildings designed to provide durable, efficient, and cost-effective solutions for a wide range of industrial, commercial, and municipal needs. We build our structures using high-quality materials and precise fabrication methods, allowing each unit to offer dependable long-term performance in environments where...
More Modular Building Manufacturers
Applications
Modular buildings, also known as prefabricated or prefab buildings, provide a cost-effective, efficient, and flexible solution for organizations and individuals seeking permanent, long-term, or temporary facilities. These structures are manufactured off-site in a controlled environment and then transported to the construction site, where they are quickly assembled. This method, known as modular construction, is gaining popularity across a variety of industries due to its speed, sustainability, and versatility.
Prefabricated modular structures can function as independent buildings or serve as extensions or partitions for existing permanent structures—a common application in manufacturing plants and industrial warehouses. The modular approach enables rapid deployment of facilities with minimal disruption to ongoing operations. This is especially valuable for organizations that require scalability, adaptability, or phased expansion.
The broad range of modular building system applications includes:
- Military barracks and government facilities: Rapidly deployable, secure, and durable modular military buildings are ideal for both domestic bases and overseas operations.
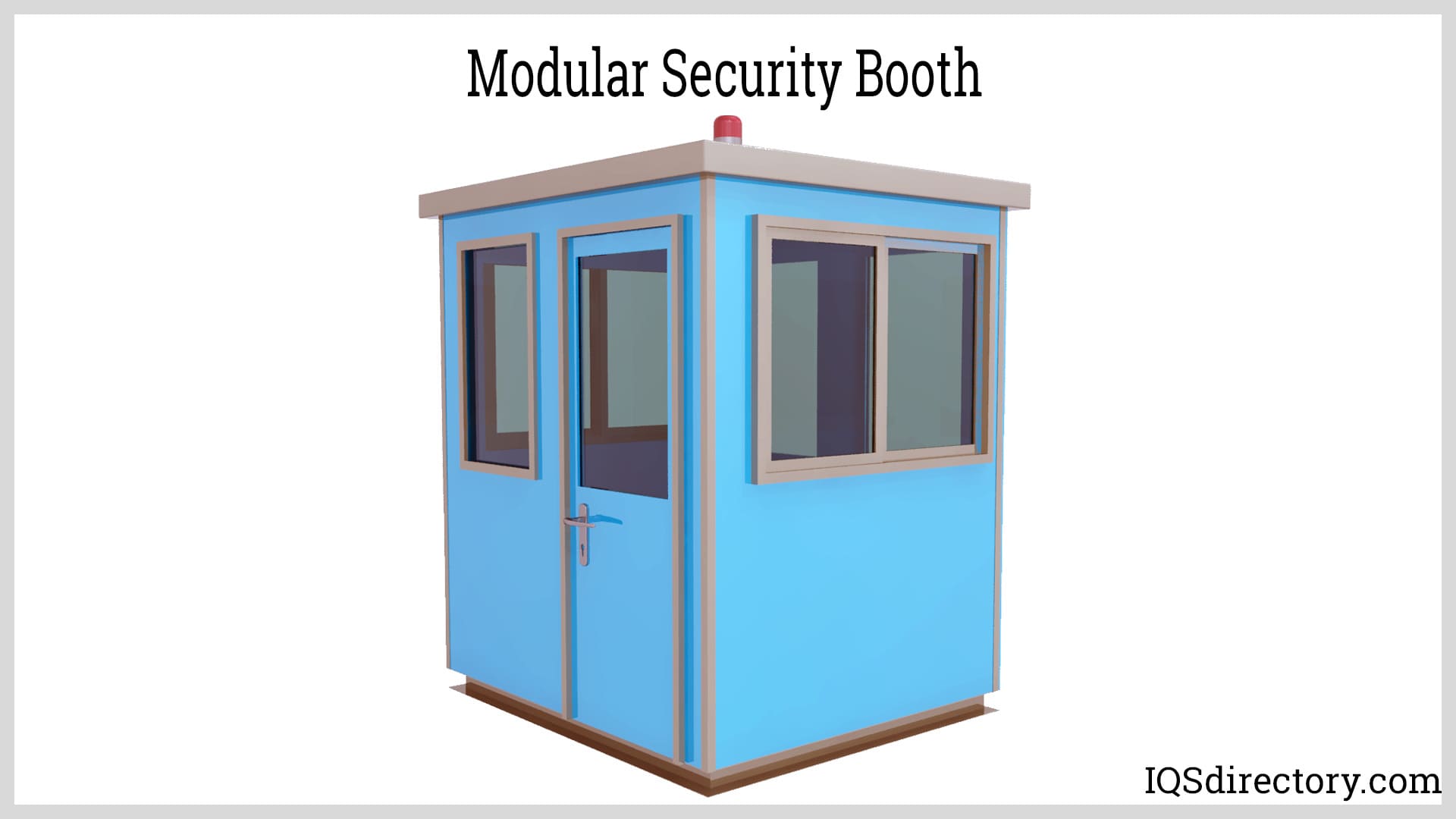
- Security booths and guard houses: Customizable, portable, and weather-resistant, these solutions are essential for access control and perimeter security.
- Disaster relief housing and emergency shelters: Quick assembly of modular homes or shelters provides immediate, safe housing for displaced populations after natural disasters.
- Temporary or mobile medical clinics and treatment centers: Healthcare providers use modular medical buildings for urgent care, COVID-19 testing, vaccination sites, and rural outreach programs.
- Educational buildings: Modular classrooms, school libraries, university dormitories, and entire educational campuses can be constructed or expanded with minimal downtime.
- Gyms, fitness centers, and recreational facilities: Modular solutions allow for fast, scalable construction of sports and community centers.
- Industrial storage buildings and warehouses: Prefabricated storage spaces can be tailored to exact specifications for logistics, inventory management, and supply chain operations.
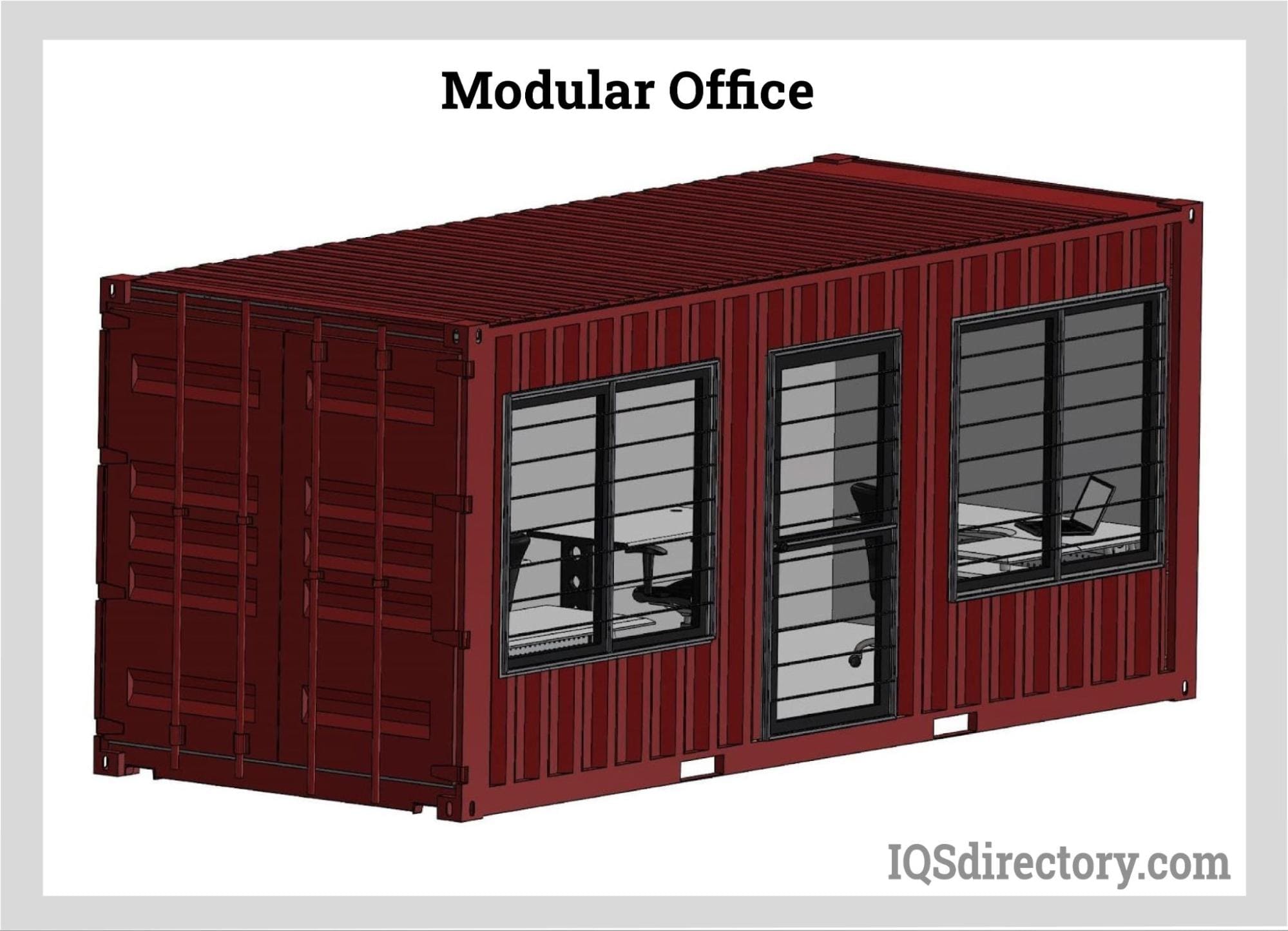
- Construction site offices and jobsite trailers: Modular offices provide comfortable, functional workspaces for project managers and crews.
- Churches, worship centers, and community spaces: Modular church buildings offer cost-effective and customizable venues for congregations.
- Permanent residential homes: Modular home construction is an increasingly popular choice for single-family and multi-family dwellings, offering affordability, quality, and design flexibility.
Considering a modular building project? What are the most common uses for modular structures in your industry? Explore our in-depth guides or contact a modular construction specialist to discover tailored solutions.
History
The concept of modular construction has evolved significantly over the past two centuries, transforming the landscape of the construction industry. While prefabrication traces its roots back to the mid-1800s, it wasn’t until the early 20th century that modular building methods gained meaningful traction. One of the earliest large-scale examples was the Sears Roebuck Company’s introduction of “build-a-home kits” in 1908. These kit homes, marketed to Americans moving westward, provided all necessary building materials and comprehensive instructions. Over 44 home styles were offered, ranging in price from $700 to $4,000. Despite the effort required for assembly, these modular kits were a massive success, with over 75,000 homes sold between 1908 and 1940.
During World War II, modular construction served a humanitarian purpose when the British government used simple, prefabricated structures as emergency shelters for citizens displaced by German bombing raids during The Blitz. These temporary modular buildings offered critical housing during times of crisis.
Post-war America saw a surge in demand for affordable, quickly constructed homes as returning soldiers and young families sought to settle down. Modular home manufacturers answered this call, rapidly producing houses that met the needs of a growing middle class. By the late 1950s, modular building companies expanded their offerings to include schools, business offices, healthcare clinics, and other commercial structures. These modular facilities provided essential infrastructure in rural and lower-income communities, delivering value through reduced construction costs and timelines.
As modular technology advanced, it attracted the attention of visionary architects, including Frank Lloyd Wright, who saw modular construction as the future of architecture. The evolution continued through the 1950s and 1980s, with manufacturers introducing larger, more customizable homes to meet changing consumer demands. By the 1990s, innovations such as overhead cranes and advanced manufacturing equipment enabled on-site assembly of increasingly sophisticated modular buildings.
Today, the modular construction industry leverages cutting-edge technologies like 3D modeling, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and CNC machines to create highly precise, intricate, and energy-efficient modules. The integration of sustainable building materials and green construction practices has further solidified modular buildings’ reputation as a modern, eco-friendly solution. As the need for rapid, scalable, and affordable construction grows, modular building solutions are poised to become even more essential in the future built environment.
Curious about the evolution of modular construction? How have modular buildings changed over time, and what innovations are shaping the industry today? Dive into our historical resources or connect with industry experts for the latest trends.
Design
Production Process
Modern modular building design begins in advanced manufacturing facilities. Here, manufacturers construct the individual modules—essentially the building blocks of the final structure—using precision assembly lines. Between 60% and 90% of the building is completed in the factory before shipment. This off-site construction process ensures consistent quality control, minimizes weather-related delays, and reduces on-site labor requirements.
The advantages of factory-controlled construction include improved safety, streamlined logistics, and reduced construction waste. Advanced techniques such as lean manufacturing, automation, and robotics play an increasingly important role in boosting efficiency and quality.
Building Materials
Modular building manufacturers utilize a diverse array of materials to satisfy architectural, structural, and environmental requirements. Common materials include:
- Steel and stainless steel: Renowned for strength, durability, and fire resistance. Frequently used in commercial, industrial, and high-rise modular structures.
- Wood and engineered timber: Offer warmth, design flexibility, and sustainability, making them ideal for residential modular homes and eco-friendly projects.
- Aluminum: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to fabricate for specialized applications.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): Highly resistant to chemicals and moisture, commonly used for modular bathrooms, kitchens, and medical facilities.
- Concrete: Provides strength, sound insulation, and thermal mass for permanent modular buildings and foundations.
- Traditional finishes: Brick facades, granite countertops, and other high-end finishes are increasingly incorporated to match or exceed the aesthetics of conventional structures.
Contrary to misconceptions, modular buildings can achieve the same—or higher—levels of quality, durability, and architectural appeal as site-built structures. Modern engineering and design tools enable customization to virtually any specification.
Considerations and Customizations
Successful modular building projects start with a thorough needs assessment. Key design considerations include:
- Aesthetic preferences: Exterior finishes, architectural style, and facade treatments to blend with existing environments.
- Functional requirements: Number of rooms, layout, floor plans, and spaces for specialized uses (labs, kitchens, classrooms, etc.).
- Local climate and weather resistance: Insulation, roofing materials, and structural reinforcements for seismic, hurricane, or snow load compliance.
- Energy efficiency: Integration of high-performance windows, insulation, LED lighting, and smart building systems.
- Building systems: Pre-installed plumbing, electrical wiring, HVAC systems, and fire safety features.
- Accessibility and compliance: ADA-compliant ramps, entrances, and restrooms.
Manufacturers usually start with standardized design templates and then offer extensive customization options, including wall thickness, ceiling height, building footprint, material selection, and modular partitioning. This flexibility allows clients to balance cost, speed, energy performance, and long-term value.
Interested in designing a modular building? What customizations and features can modular construction provide for your project? Use our interactive design tools or schedule a consultation with our modular architects.
Types
With the rise of modular construction, a variety of modular building types have emerged to serve diverse market needs. Understanding these categories is key to choosing the best solution for your project:
- Portable buildings: Also known as mobile modular buildings, these structures are engineered for easy relocation. Ideal for temporary offices, classrooms, field clinics, and event spaces, portable buildings can be disassembled and moved as needs change, offering unmatched flexibility.
- Permanent modular buildings: Designed for long-term use, these structures employ the same materials and construction standards as traditional site-built buildings. Examples include permanent modular schools, apartment complexes, and medical facilities. They offer rapid occupancy and long-term durability.
- Commercial modular buildings: Custom-built for businesses, these include offices, conference centers, retail stores, libraries, and more. Commercial modular construction must adhere to local building codes, zoning regulations, and industry standards. Concrete foundations and advanced MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems are common.
- Modular homes: A subset of permanent modular buildings, modular homes differ from mobile homes or manufactured housing by adhering to higher construction standards and offering greater design flexibility. Modular homes can be custom-built to match any style or size, from small cottages to luxury estates.
- Modular additions: These are extensions or new rooms added to an existing building. While it’s easiest to add modules to existing modular structures, integration with conventional buildings is possible. Common modular additions include school classroom partitions, hospital wings, or expanded office spaces.
Looking for the right modular solution? Which type of modular building best meets your space, budget, and timeline requirements? Compare different modular building types or request a free needs assessment from our experts.
Advantages
Modular buildings deliver a host of compelling benefits that make them an increasingly preferred choice for construction projects worldwide:
- Reduced construction time: Off-site fabrication and parallel site preparation can cut project timelines by 30-50% compared to traditional building methods.
- Cost savings: Manufacturing efficiencies, reduced labor costs, and minimized project delays translate into significant budget advantages for modular construction.
- Consistent quality: Controlled factory environments ensure precise workmanship, rigorous quality assurance, and fewer defects or rework issues.
- Environmental sustainability: Modular construction generates up to 80% less waste than traditional construction, supports material recycling, and reduces site disruption and energy consumption.
- Flexibility and scalability: Easily expand, reconfigure, or relocate modular buildings to adapt to changing needs, saving time and resources over the building’s lifecycle.
- Safer job sites: Factory-based production limits on-site hazards, reduces weather-related risks, and enhances worker safety.
- Faster return on investment: Quicker project completion means earlier occupancy and revenue generation for businesses and organizations.
- High-performance design: Modular buildings can incorporate advanced insulation, energy-efficient systems, smart technology, and healthy building materials.
Want to maximize the benefits of modular construction? How can modular buildings lower your project costs and accelerate your timeline? Request a detailed ROI analysis or case study from our team.
Accessories
To further enhance your modular building, manufacturers offer a wide selection of accessories and upgrades tailored to your application, including:
- Roof vents and skylights for improved ventilation and natural lighting
- Partition walls and flexible room dividers
- Integrated plumbing fixtures and bathroom modules
- State-of-the-art heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems
- Energy-efficient LED lighting and smart controls
- Storm windows, hurricane panels, and weatherproof doors
- Electrical outlets, data ports, and charging stations
- Security systems, fire alarms, and access control technology
Need specialized features? What accessories and upgrades are available for modular buildings in your sector? Explore our accessory catalog or speak with a modular solutions advisor.
Installation
The modular building installation process is meticulously coordinated to ensure safety, efficiency, and project success. After manufacturing, modules are transported to the site—typically via flatbed trucks—and positioned using cranes onto the building’s prepared foundation. Modules may be stacked for multi-story construction or arranged side-by-side or end-to-end, depending on the floor plan.
Once in place, the modules are securely fastened using a combination of cables, straps, split bolts, turnbuckles, and, for some applications, all-bolted steel floors. Connections are sealed and integrated, with final systems (plumbing, electrical, HVAC) completed on-site. Even if prefab buildings arrive in a specific arrangement, they can often be reconfigured or expanded as operational needs change.
Professional installation teams ensure that all work meets local codes and manufacturer specifications, delivering a turnkey solution that is ready for immediate occupancy.
Planning a modular project? What is the typical timeline for modular building installation, and what site preparations are needed? Download our installation checklist or consult with our project managers for tailored advice.
Standards
Modular buildings are held to the same rigorous building codes and regulatory standards as traditional site-built structures. Compliance includes:
- ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act): Ensures accessibility for all occupants, including ramps, elevators, and accessible restrooms.
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration): For modular medical facilities, compliance with health and safety standards is mandatory.
- IBC (International Building Code) and local building codes: Regulate fire safety, structural integrity, electrical systems, and occupancy.
- Energy codes: Mandate insulation values, energy efficiency, and green building practices.
- Industry-specific standards: Educational, healthcare, and commercial projects may have additional requirements for safety, ventilation, and specialized use.
To ensure your modular building project is compliant, consult with both your manufacturer and local zoning authorities. What building codes and standards apply to your modular building project? Access our compliance resources or speak with a regulatory specialist for assistance.
Things to Consider
Proper planning is vital for a successful modular building project. Before placing an order, follow these steps to streamline your process and avoid unnecessary complications:
- Research zoning restrictions and permits: Understand local, state, and federal regulations governing modular building placement, use, and appearance.
- Verify construction standards and codes: Ensure your project complies with all applicable building codes, energy standards, and industry-specific regulations.
- Identify project requirements: Document your space needs, timeline, budget, accessibility requirements, and desired features.
- Develop a list of specifications: Include preferences for materials, finishes, foundation type, structural requirements, environmental factors, and future scalability.
- Shortlist reputable modular building manufacturers: Review company profiles, certifications, project portfolios, and customer reviews. Seek manufacturers with experience in your sector.
- Engage with customer service representatives: Use your specifications as a guide to discuss design options, materials, foundation needs, climate resilience, wiring, and building codes. Clarify budget constraints and project timelines.
- Compare proposals: Evaluate quotes, designs, customizations, warranties, and after-sales support from multiple providers to make an informed decision.
Ready to take the next step? How do you choose the right modular building manufacturer for your needs? Browse our curated list of top-rated manufacturers or request personalized recommendations.
When speaking with modular building experts, don’t hesitate to ask about:
- Material selection and environmental performance
- Structural requirements for your site and climate
- Integration with existing buildings or infrastructure
- Long-term maintenance, warranties, and support
- Financing options, leasing, and insurance
- Turnkey project management and installation services
After gathering all necessary information and comparing your options, you will be equipped to select the best modular building solution and partner for your project.
Have more questions? What should you ask before purchasing a modular building? Explore our buyer’s guide or contact our team for expert advice.
What are the most common applications for modular buildings?
Modular buildings are used for military barracks, security booths, disaster relief housing, medical clinics, educational buildings, gyms, industrial storage, construction offices, churches, and permanent residential homes. They provide scalable, adaptable, and rapid solutions for both temporary and permanent space needs across many industries.
How has modular building construction evolved over time?
Modular construction began in the 19th century with early prefabricated structures and grew in popularity with Sears kit homes in the early 1900s. It played a major role in providing shelter during wartime and post-war housing surges. Today, advancements like 3D modeling, BIM, CNC machines, and sustainable materials have made modular buildings more precise, efficient, and eco-friendly than ever.
What materials are commonly used in modular buildings?
Common materials include steel, stainless steel, wood, engineered timber, aluminum, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), concrete, and high-end finishes like brick and granite. The choice of materials depends on structural, architectural, and environmental requirements, and allows for high levels of customization and durability.
What are the key advantages of modular buildings?
Modular buildings offer reduced construction time, cost savings, consistent quality, environmental sustainability, flexibility, safer job sites, a quicker return on investment, and high-performance design options including energy-efficient systems and smart technology integration.
How is a modular building installed and what is the typical timeline?
Modules are manufactured off-site, transported to the site, and placed onto prepared foundations using cranes. Final connections for plumbing, electrical, and HVAC are completed on-site. Professional installation ensures compliance with local codes, and the entire process is much faster than traditional construction.
What standards and codes must modular buildings comply with?
Modular buildings comply with the same standards as site-built structures, including the ADA, FDA (for medical facilities), IBC and local building codes, energy codes, and project-specific industry standards. Compliance ensures safety, accessibility, energy efficiency, and regulatory approval.
What should you consider before buying a modular building?
Before purchasing, research zoning restrictions, verify construction codes, identify project requirements, finalize specifications, choose reputable manufacturers, engage with customer service, and compare proposals. Consider integration with existing structures, long-term support, financing options, and project management services.





 55 Gallon Drums
55 Gallon Drums Floor Gratings
Floor Gratings Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Plastic Containers
Plastic Containers Plastic Pallets
Plastic Pallets Plastic Tanks
Plastic Tanks Steel Shelving
Steel Shelving Stainless Steel Tanks
Stainless Steel Tanks Storage Racks
Storage Racks Work Benches
Work Benches Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services